« Previous
Next »
« Previous
Next »
MICROSOFT EXCEL 2013
Financial
- FV() Returns the future value of an investment based on periodic, constant payments and a constant interest rate. Syntax : FV(rate,nper,pmt,pv,type)
- Rate is the interest rate per period.
- Nper is the total number of payment periods in an annuity.
- Pmt is the payment made each period; it cannot change over the life of the annuity. Typically, pmt contains principal and interest but no other fees or taxes. If pmt is omitted, you must include the pv argument.
- Pv is the present value, or the lump-sum amount that a series of future payments is worth right now. If pv is omitted, it is assumed to be 0 (zero), and you must include the pmt argument.
- Type is the number 0 or 1 and indicates when payments are due. If type is omitted, it is assumed to be 0.
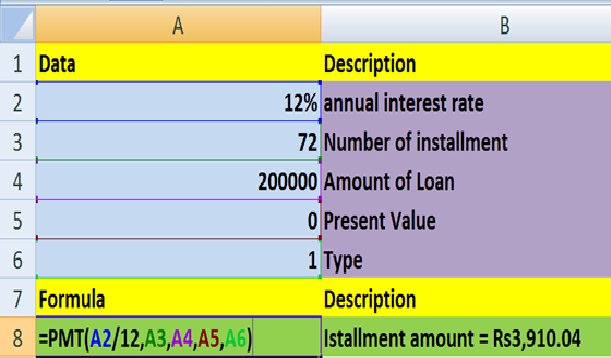
- PMT() Calculates the payment for a loan based on constant payments and a constant interest rate. Syntax : PMT(rate,nper,pv,fv,type) Rate is the interest rate for the loan. Nper is the total number of payments for the loan. Pv is the present value, or the total amount that a series of future payments is worth now; also known as the principal. Fv is the future value, or a cash balance you want to attain after the last payment is made. If fv is omitted, it is assumed to be 0 (zero), that is, the future value of a loan is 0. Type is the number 0 (zero) or 1 and indicates when payments are due.
| Set type equal to | If payments are due |
|---|---|
| 0 | At the end of the period |
| 1 | At the beginning of the period |
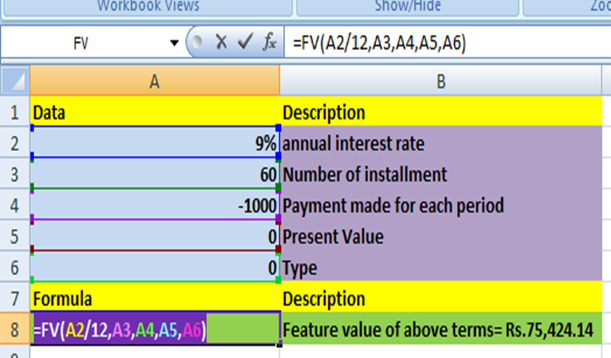
| Set type equal to | If payments are due |
|---|---|
| 0 or omitted | At the end of the period |
| 1 | At the beginning of the period |